The frog food chain consists of frogs as secondary consumers, feeding on insects and small invertebrates. Frogs play a vital role in maintaining the ecosystem’s balance by controlling insect populations.
Frogs are an essential part of the food chain, serving as secondary consumers that feed on insects and small invertebrates. By preying on these organisms, frogs help regulate their populations, preventing overgrowth that could disrupt the ecosystem. Understanding the dynamics of the frog food chain is crucial for preserving biodiversity and ensuring the health of our environment.
Frogs’ diet varies depending on their life stage, with tadpoles consuming algae and adult frogs primarily feeding on insects. This intricate web of interactions highlights the interconnectedness of species in nature, emphasizing the significance of each organism’s role in sustaining a healthy ecosystem.

Credit: www.pinterest.com
Introduction To Frog Food Chains
The frog food chain is an important aspect of ecosystems. Frogs play a crucial role as both predators and prey in the food chain. As predators, they feed on insects such as flies, moths, snails, slugs, and worms. They use their long tongues and sticky saliva to catch their prey. As prey, tadpoles eat algae in the ponds they grow in and later feed on plants and small insects. Adult frogs generally have a carnivorous diet consisting of small invertebrates, but there are also omnivorous species that feed on plant matter. The food chain in an ecosystem refers to the order of events where one living organism eats another, and later that organism is consumed by another larger organism, forming a flow of nutrients and energy at different trophic levels.
Frog Life Stages And Diet
Tadpole dietary habits: Tadpoles primarily feed on algae in their habitat, using it as their main source of nutrition as they grow and develop into adult frogs.
Dietary evolution from tadpole to adult frog: As tadpoles transition into adult frogs, their diet evolves to include small invertebrates such as insects, flies, moths, snails, and worms. Some adult frogs may also consume plant matter, displaying an omnivorous diet. The food chain in the ecosystem reflects the progression of nutrients and energy from one organism to another at different trophic levels.
Common Prey For Frogs
Frogs primarily feed on insects such as flies, moths, and other small invertebrates. They catch their prey using their long tongues and sticky saliva. Additionally, tadpoles consume algae in the ponds they inhabit and as they grow, they start feeding on plants and small insects.
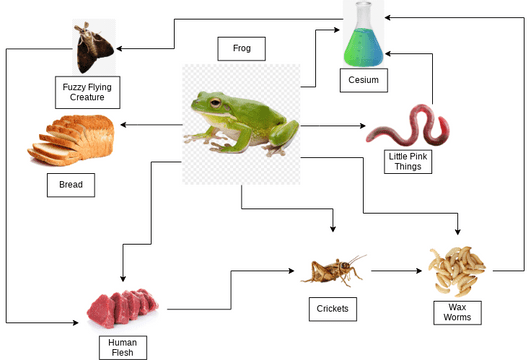
Credit: online.visual-paradigm.com
Frog Predators In The Wild
The frog is a secondary consumer in the food chain, which means that it depends on primary consumers for its food, such as insects. Birds of prey, reptiles, and mammals are the main predators of frogs in the wild. Birds of prey, such as hawks and eagles, hunt for adult frogs, while reptiles, such as snakes and lizards, and mammals, such as foxes and raccoons, prey on both adult frogs and tadpoles.
It is important to note that frogs play a crucial role in the food chain as they are both predator and prey. As a predator, they feed on insects, which helps to control their populations. As prey, they provide a food source for larger animals.
The Trophic Levels Explained
Exploring the frog food chain reveals a fascinating ecosystem where tiny insects sustain frogs. From tadpoles munching on algae to adult frogs devouring insects, each step in this trophic level showcases nature’s intricate balance of predator and prey.
The frog food chain is a complex system that involves several trophic levels. In this ecosystem, frogs act as secondary consumers, feeding on primary consumers such as insects, snails, and worms. The energy flow through trophic levels follows a specific pattern, where producers such as plants provide energy to primary consumers, who in turn provide energy to secondary consumers. Adult frogs have a carnivorous diet, while tadpoles feed on algae and small insects. The food chain in the ecosystem refers to the order of events where one living organism eats another organism, and later that organism is consumed by another larger organism. This flow of nutrients and energy occurs at different trophic levels. Overall, the frog food chain plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
Credit: www.baamboozle.com
Adaptations For Feeding
The frog food chain involves various adaptations for feeding. Frog tongues and capture techniques enable them to catch prey effectively. Additionally, digestive adaptations allow frogs to process their food efficiently. Adult frogs generally have a carnivorous diet consisting of small invertebrates. Some frog species are omnivorous and may consume plant matter as well. Tadpoles, on the other hand, primarily feed on algae in their growing environment and transition to consuming plants and small insects as they develop. This diverse diet showcases the adaptability of frogs within the food chain, and their role as secondary consumers is essential in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
Threats To Frog Populations
Frogs are facing threats to their populations due to habitat degradation and pollution. Habitat degradation, caused by deforestation and urbanization, disrupts the natural ecosystems where frogs live. Pollution, including chemicals and waste, impacts the food chain by contaminating the water and affecting the availability of prey for frogs. These threats have significant implications for the survival of frog populations and the overall balance of the ecosystem.
Conservation And The Role Of Frogs
Conservation and the role of frogs in ecosystem balance and frog conservation is essential for public awareness and education. Frogs play a vital role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. They act as indicators of environmental health and help control insect populations, contributing to agricultural and human health. Furthermore, the conservation of frogs is crucial for preserving biodiversity and ensuring the sustainability of ecosystems. Educating the public about the importance of frogs in the food chain and their conservation is necessary for promoting environmental stewardship and sustainable practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Type Of Consumer Is The Frog In The Food Chain?
The frog in the food chain is a secondary consumer, relying on insects as its primary food source.
What Is The Food Of Frogs?
Frogs primarily eat insects, such as flies and moths, along with snails, slugs, and worms. Tadpoles consume algae and later feed on plants and small insects as they grow.
What Is The Food Classification Of A Frog?
Frogs are classified as carnivores, feeding on small invertebrates, with some species being omnivorous and consuming plant matter.
What Is The Food Chain In The Ecosystem?
A food chain in an ecosystem is the sequence where one organism eats another for energy.
Conclusion
Frogs play a crucial role in the food chain as secondary consumers, depending on insects for sustenance. Their diet consists of small invertebrates, showcasing their carnivorous nature. Understanding the frog food chain sheds light on the intricate balance of ecosystems.
Embracing these insights enhances our appreciation for nature’s interconnected web.
